Galerie Yuri

Nearly 100 years ago a young astronomer named Cecilia Payne changed the way we see the stars in the sky because she was able to look into their burning heart and see.
Stars—facts and information
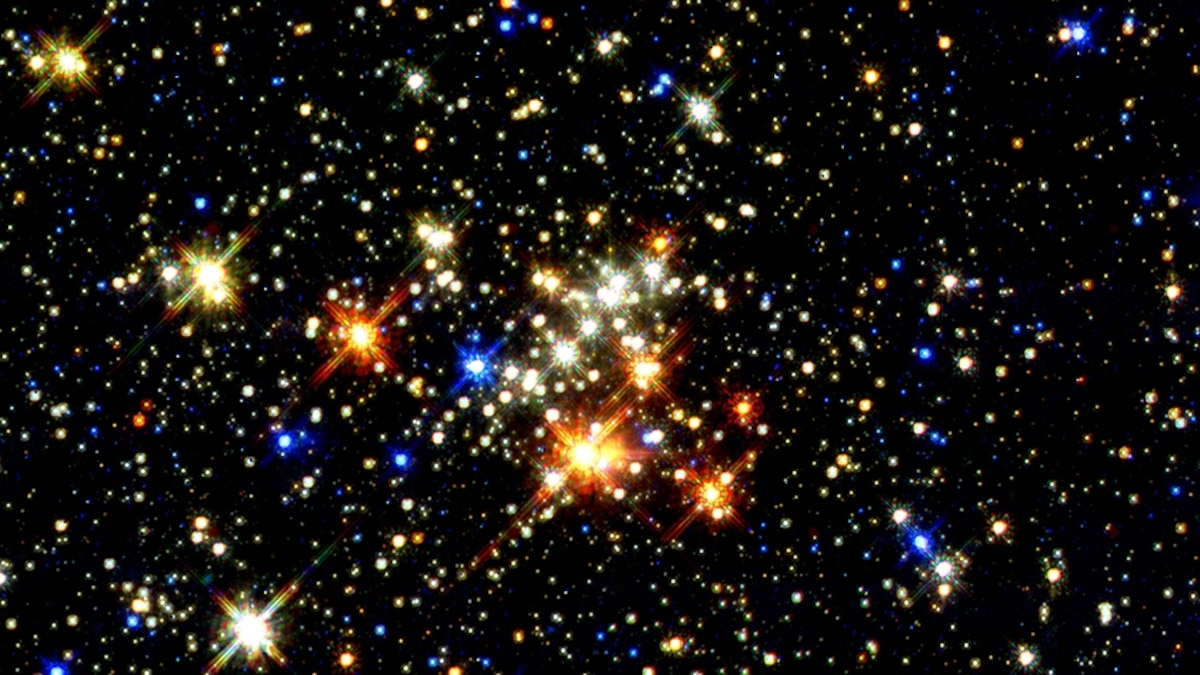

A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun.Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names.
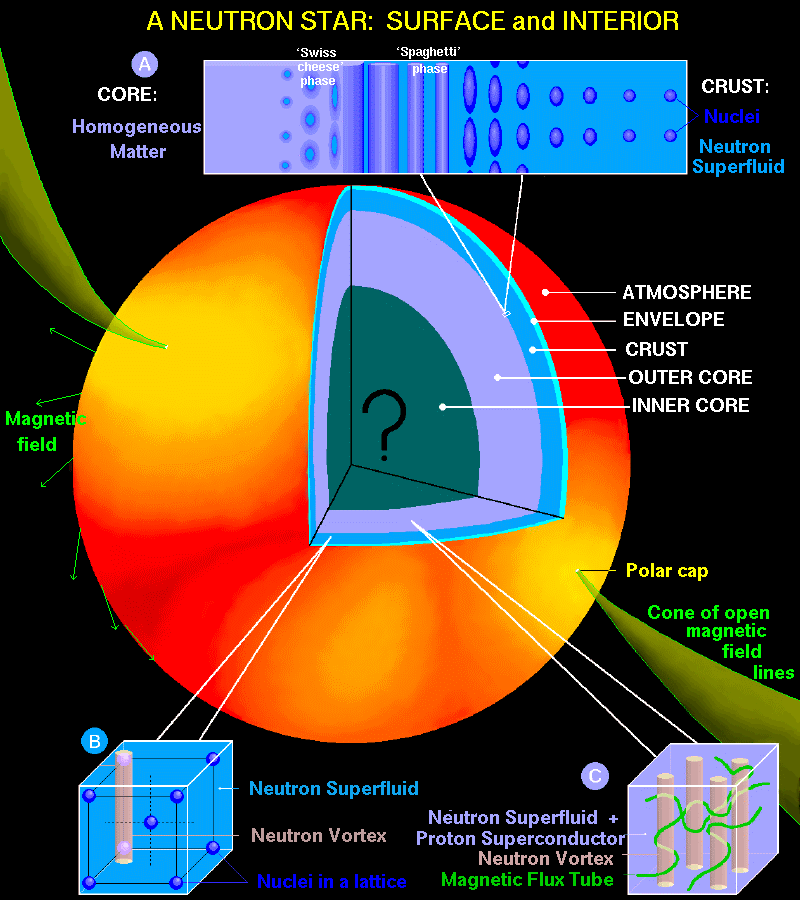
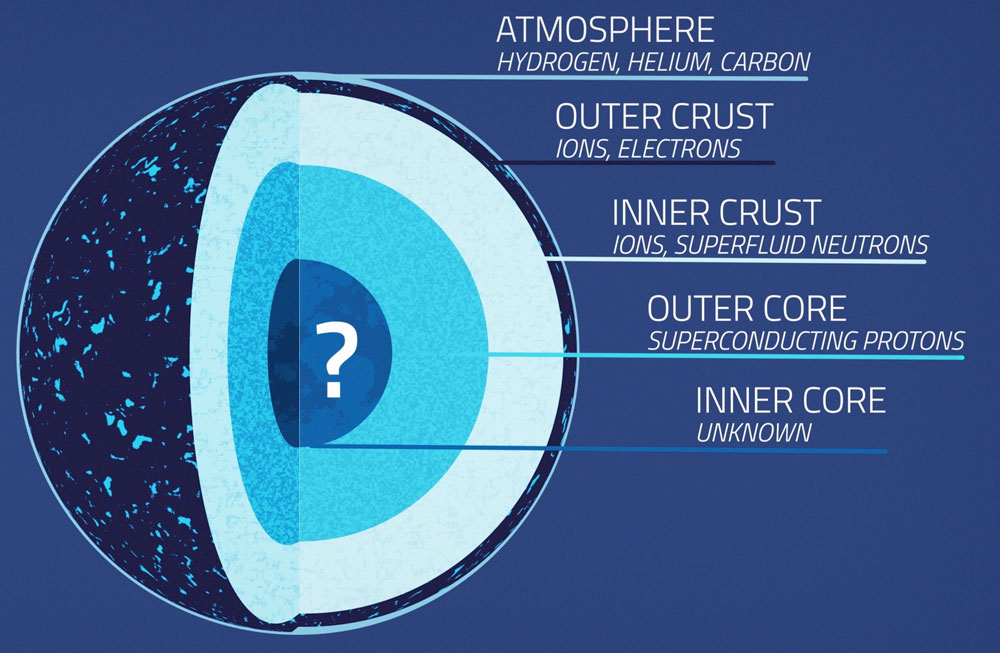
Neutron stars
A star is born. The life cycle of a star spans billions of years. As a general rule, the more massive the star, the shorter its life span. Birth takes place inside hydrogen-based dust clouds.
The stellar evolution of stars — Science Learning Hub

Key Facts & Summary. Stars are huge celestial bodies made mostly of hydrogen and helium that produce light and heat from the churning nuclear forges inside their cores. Aside from our Sun, stars appear as dots of light in the sky. Each and every one of them is light-years away from us and much brighter than our own star, the Sun.
Stars Facts For Kids Seven Types, What, Formation, Size & Age
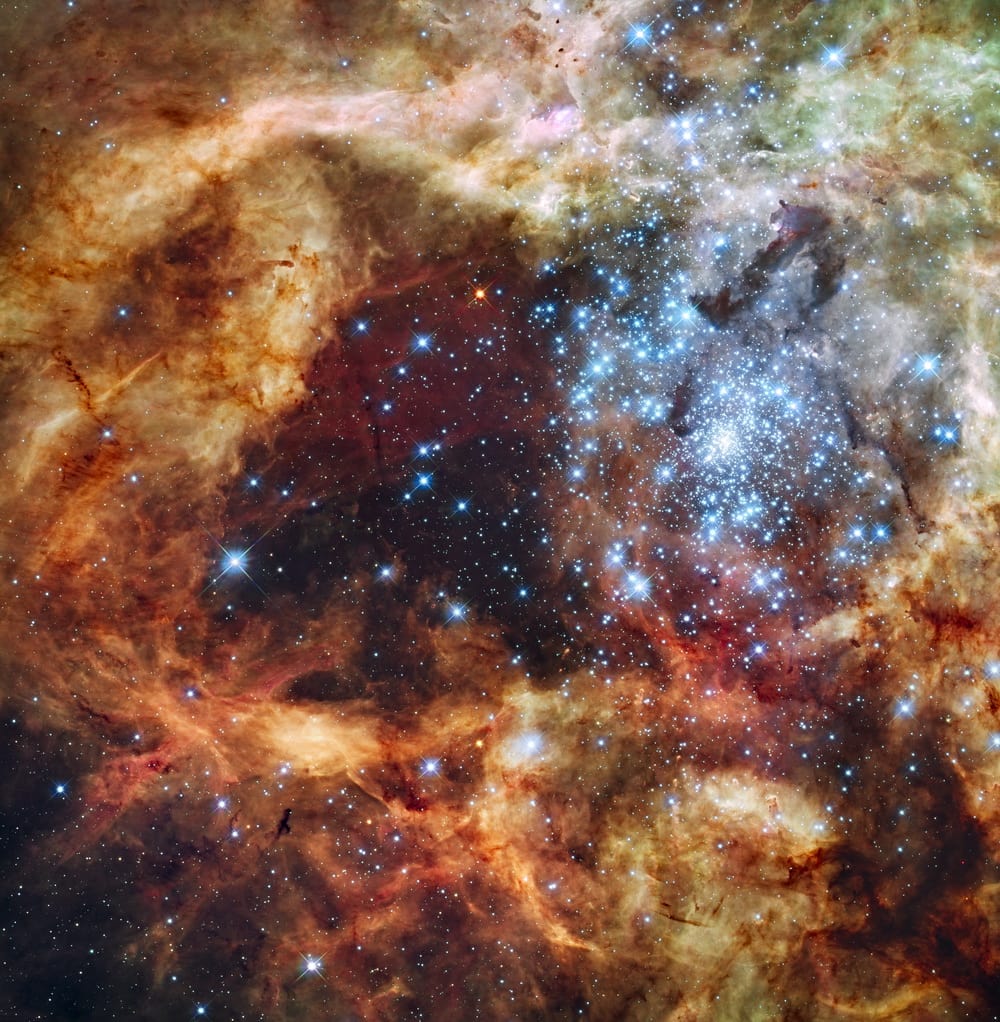
The observations reveal the violent process of star birth that produces intense ultraviolet radiation and shock fronts. The radiation clears out cavities in stellar nursery clouds and erodes material from giant gas pillars that are incubators for fledgling stars. A jet from a newly formed star flares into the shining depths of reflection nebula.
What’s Inside Neutron Stars? Sky & Telescope Sky & Telescope
Stars form in large clouds of gas and dust called molecular clouds. Molecular clouds range from 1,000 to 10 million times the mass of the Sun and can span as much as hundreds of light-years. Molecular clouds are cold which causes gas to clump, creating high-density pockets. Some of these clumps can collide with each other or collect more matter.
HOW ARE STARS MADE? by Felix Carlen

What Stars Are Made Of provides both an accessible introduction to and an expansive context for the life and work of Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin, one of the most brilliant astrophysicists of the twentieth century. The sharing of stories like Payne-Gaposchkin's will reshape the future of science so that all aspiring scientists may reach their full potential as we continue to explore the universe.
Facts about Stars for Kids Definition, Formation and Lives » Selftution
NASA Grant Brings Students at Underserved Institutions to the Stars. article 1 week ago. 2 min read. Washington State High Schooler Wins 2024 NASA Student Art Contest. article 1 week ago. Highlights. 4 min read. NASA Mission Strengthens 40-Year Friendship.
Look up to the stars

The answer is that we must rely on their light. We know that a star's colour gives away its temperature (Ribeiro, 2015), but how do we know what stars are made of? Again, star light, or more specifically, the star's spectrum, is the answer. At the Science on Stage festival held in London in June 2015, a discussion about combining hands-on.
20 amazing facts about stars How It Works

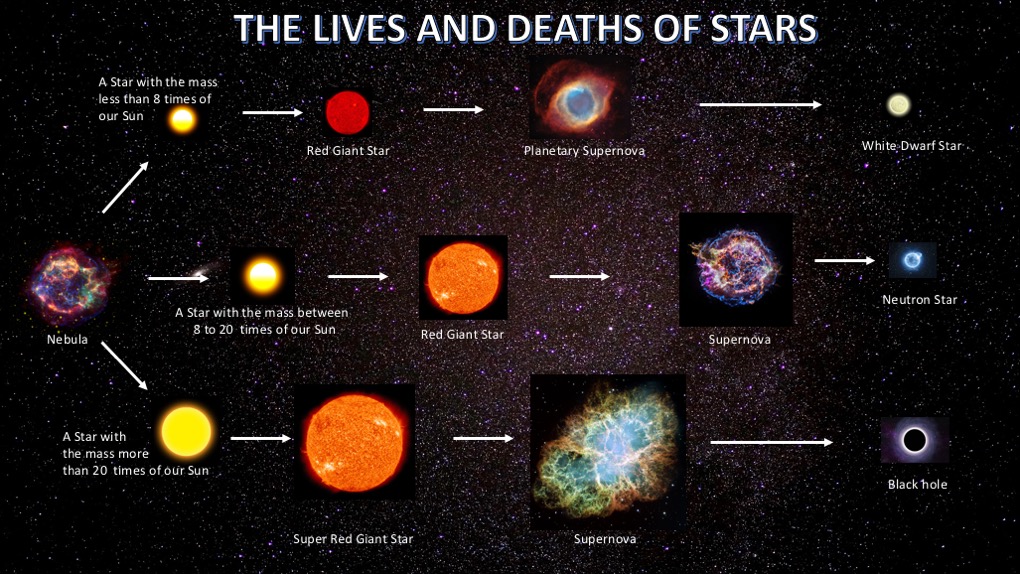
A star's mass determines its temperature and luminosity, and how it will live and die. The more massive a star is, the hotter it burns, the faster it uses up its fuel, and the shorter its life is. The hottest and most massive stars are blue and bright, while the coolest and least massive stars are red and dim.
What's a Star and What Are They Made Of?

Stars are the source of almost all of the light our eyes see in the sky. Nuclear fusion is what makes a star what it is: the creation of new atomic nuclei within the star's core. Many of stars' properties — how long they live, what color they appear, how they die — are largely determined by how massive they are. The study of stellar structure and evolution is dedicated to understanding.
15 amazing facts about stars How It Works
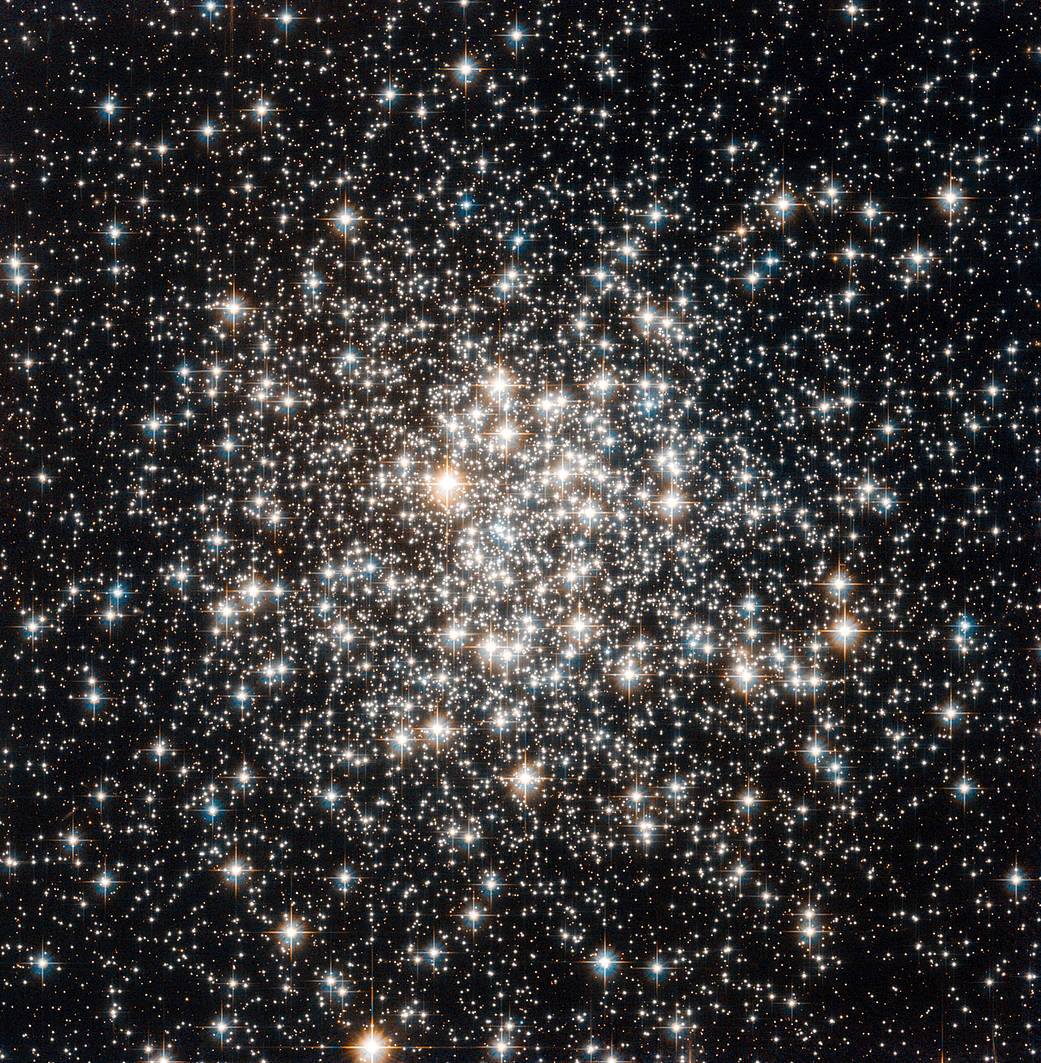

Stars are also classified by their luminosity under the Morgan-Keenan system. The largest and brightest classes of stars have the lowest numbers, given in Roman numerals — Ia is a bright.
Curious Kids how are stars made?
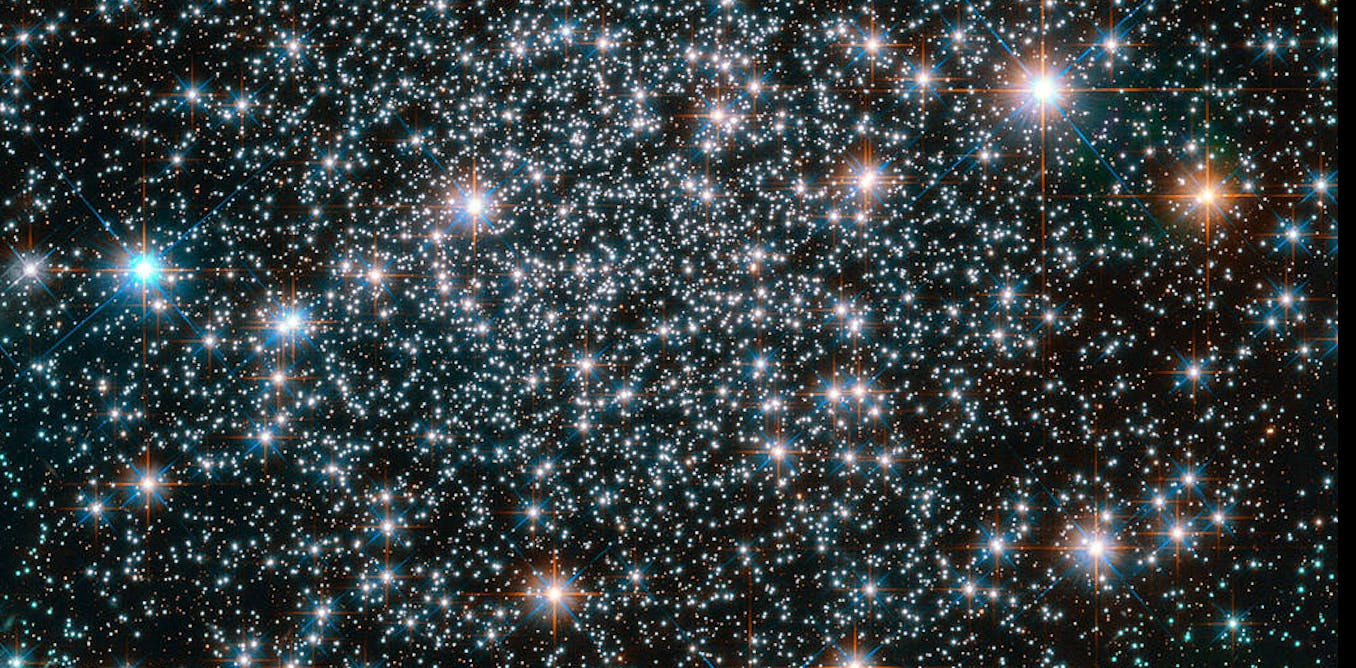

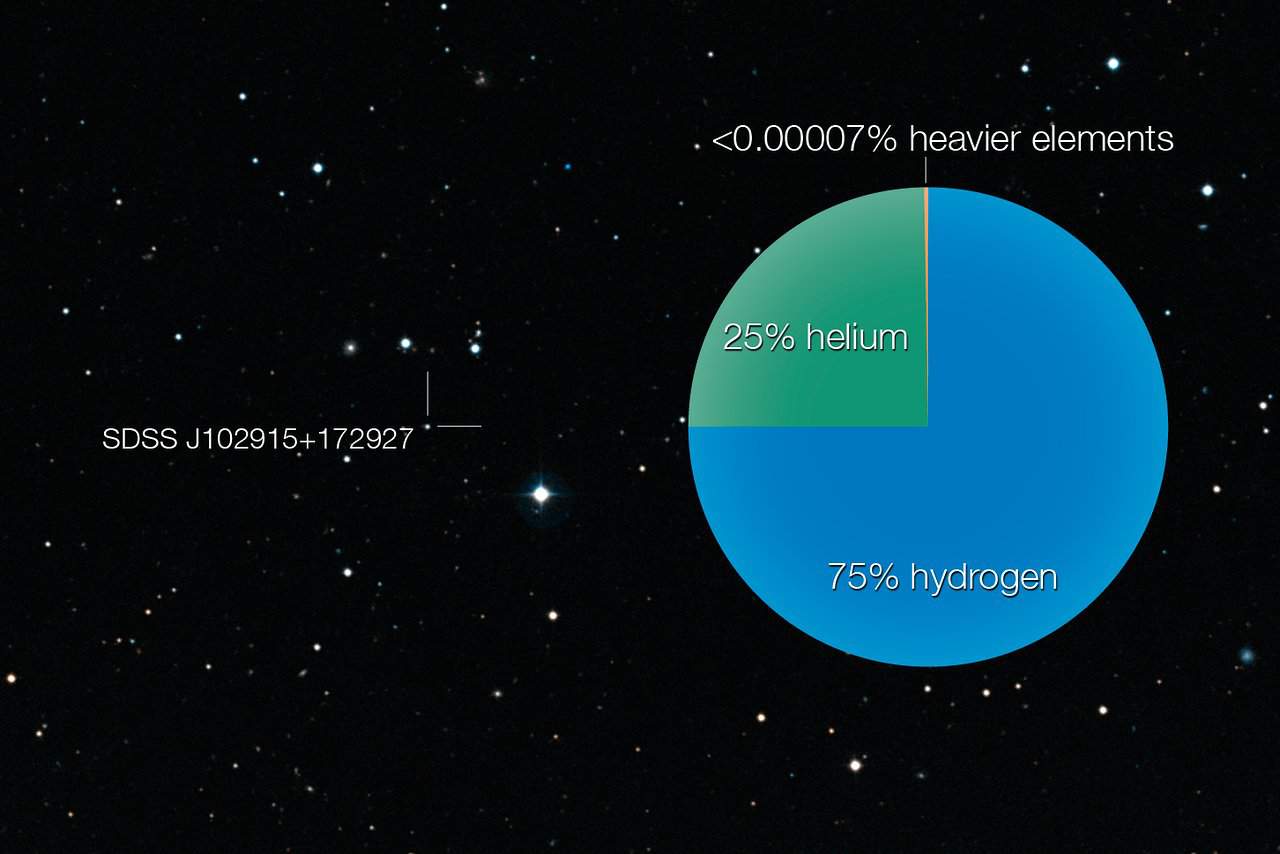
Stars everywhere are made of the same stuff: 3/4 hydrogen and 1/4 helium. It's the stuff left over from the formation of the Universe, and one of the most elegant pieces of evidence to help.
How Do We Know What Stars Are Made Of? NSTA

First things first: stars are definitely not fireflies or dead kings of the past, as proposed by Timon and Simba, Pumbaa's co-conspirators in scientific speculation. That we know for sure, according to Scott. "Stars are basically balls of very, very hot gas, including gaseous hydrogen and other elements, all of which can be recreated in.
HOW ARE STARS MADE? by Felix Carlen

Even though our Sun is unbelievably hot, compared to other stars, the Sun is one of the cooler stars. Scientists have learned that a star's color corresponds to its temperature. The hottest stars are blue and the coolest are red. Yellow stars, like the Sun, are closer to red and are thus cooler, even though they're still incredibly hot!
What's a Star and What Are They Made Of?
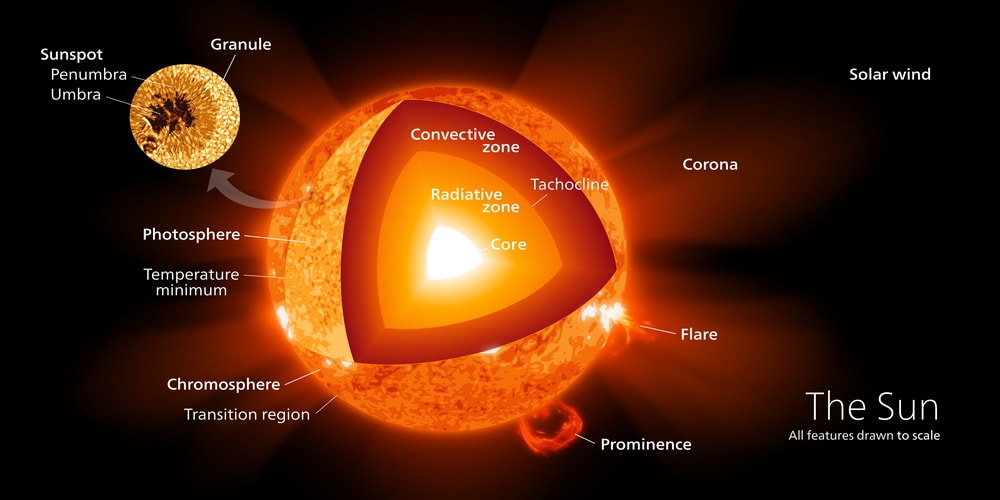
Star is a comprehensive article on Britannica that explains the nature, characteristics, and evolution of stars, the luminous celestial bodies of gas that emit light and heat. The article covers the sizes, energetics, temperatures, masses, and chemical compositions of stars, as well as the classification and life cycle of different types of stars. Whether you are interested in astronomy.
.